Emotet is a very well-known malware family that was first discovered in 2014, and it remains one of the most prevalent threats of the decade. Sometimes referred to as Geodo or Feodo, Emotet is Windows-based malware that first appeared as a banking Trojan. Since then, Emotet has evolved into modular malware that performs various functions, including information stealing, spambot activity and loading other malware.
In 2021 the servers used for Emotet were disrupted through global police action in Germany and Ukraine and brought under the control of law enforcement.
On 14 November 2021, new Emotet samples emerged that were very similar to the previous bot code, but with a different encryption scheme that used elliptic curve cryptography for command and control communications. The new Emotet infections were delivered via TrickBot, to computers that were previously infected with TrickBot, and soon began sending malicious spam email messages with macro-laden Microsoft Word and Excel files as payloads.
There are multiple very good analyses of Emotet versions and we wanted to have a look at one of the most recent versions (as of November 2022).
Analysis
The following image shows a MITRE ATT&CK view of all the different techniques that happened during the Emotet infection. The Emotet detonation was made just by opening a malicious Excel spreadsheet that includes a malicious macro.
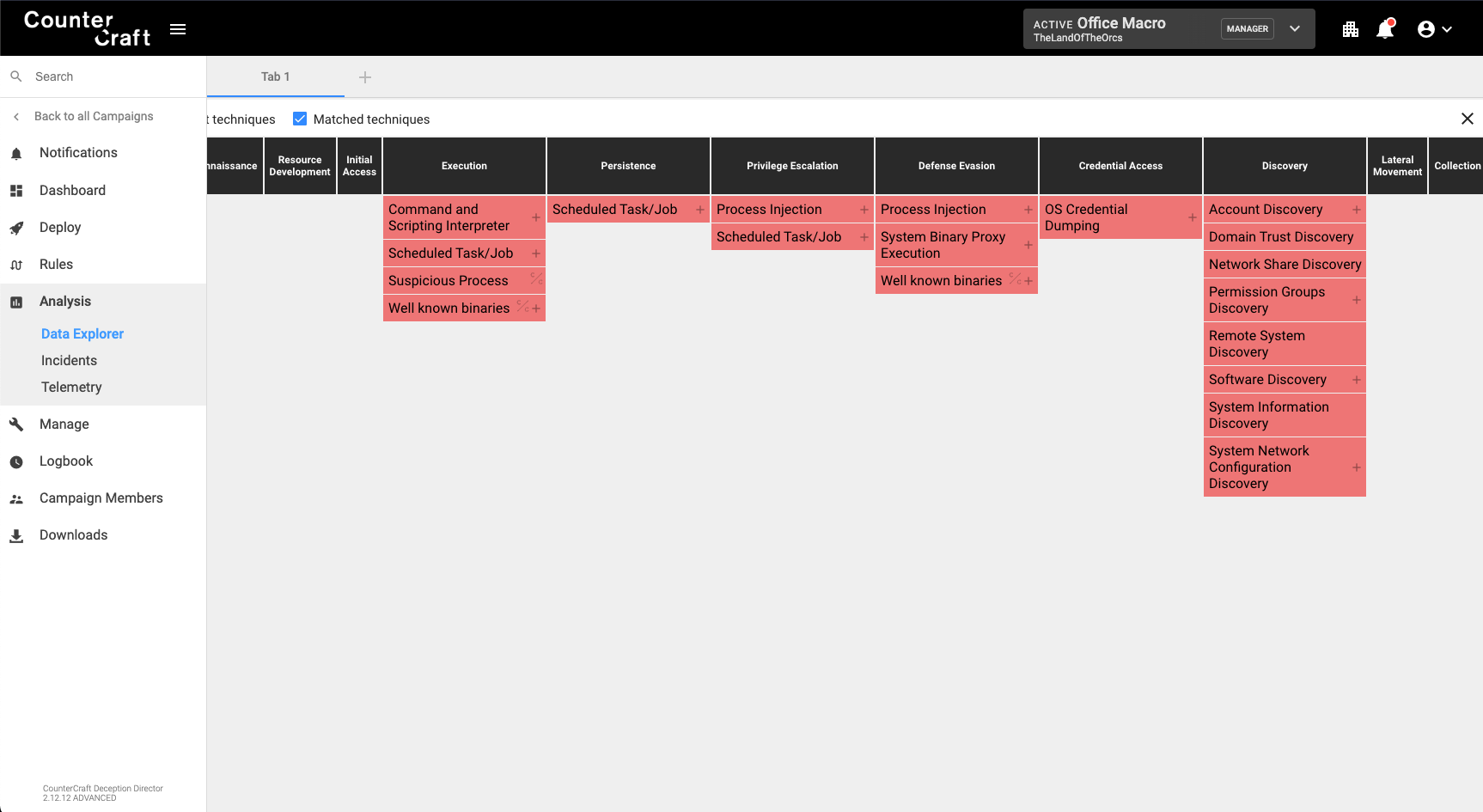
As we can see in the screenshot, the infection triggered a number of executions, that included techniques for persistence, defense evasion, credential access, discovery and command and control.
In the following section there is a detailed timeline of the infection process, but a good summary of what happened is the following:
- – Excel spreadsheet is opened.
- – The malicious macro connects to different C2s and downloads some DLL and EXE files.
- – The malicious macro uses ‘regsvr32.exe’ for loading those DLL files.
- – One of the downloaded DLLs establishes persistence by adding a new registry key to the Windows CurrentVersion/Run registry path.
- – One of the downloaded DLLs also establishes persistence by creating a scheduled task.
- – One of the downloaded DLLs receives different commands to gather information about the infected hosts (domains, users, code page/language, etc.)
- – Some of the downloaded EXE and DLL files are used for self-propagation (sending emails with malicious Office documents).
Events timeline
Once we opened the malicious Excel document (at 14:12:53) we could see the following events.
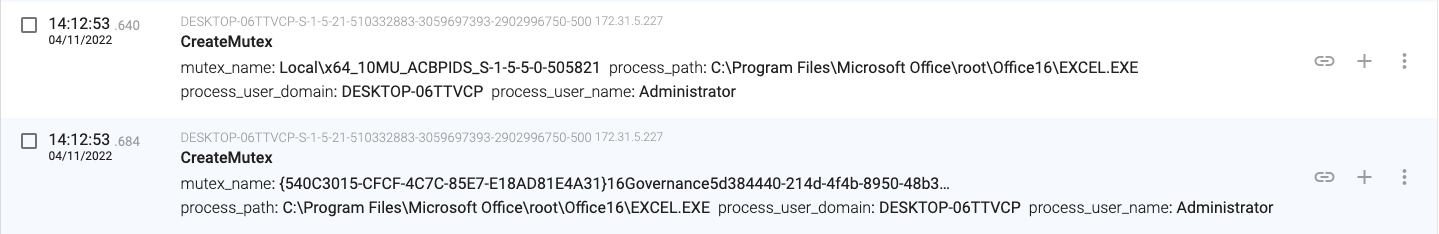
14:12:53.640, the macro will create two different mutexes.
14:12:54.673, the macro creates a temporary file.

14:12:54.766, the macro connects to the named pipes for RPC over SMB (wkssvc and srvsvc)


14:12:55.628, the macro creates code in memory that will execute.

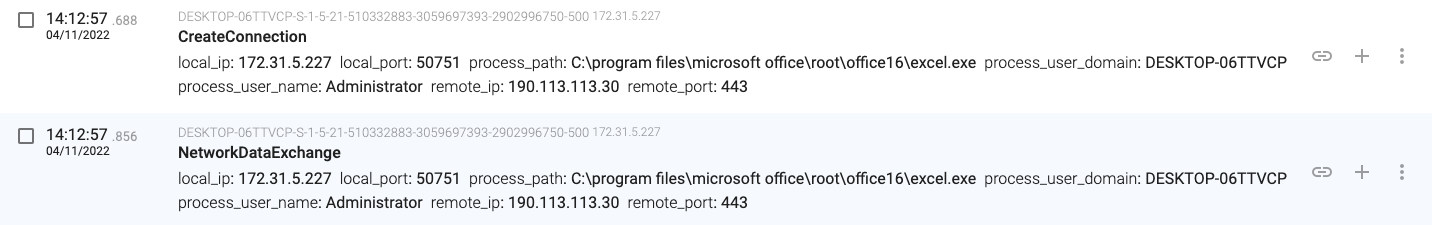
14:12:57.486, the macro sends a DNS request querying for ‘audioselec.com’.

14:12:57.688, the macro connects and downloads content from the ‘audioselec.com’ IP address 190.113.113.30
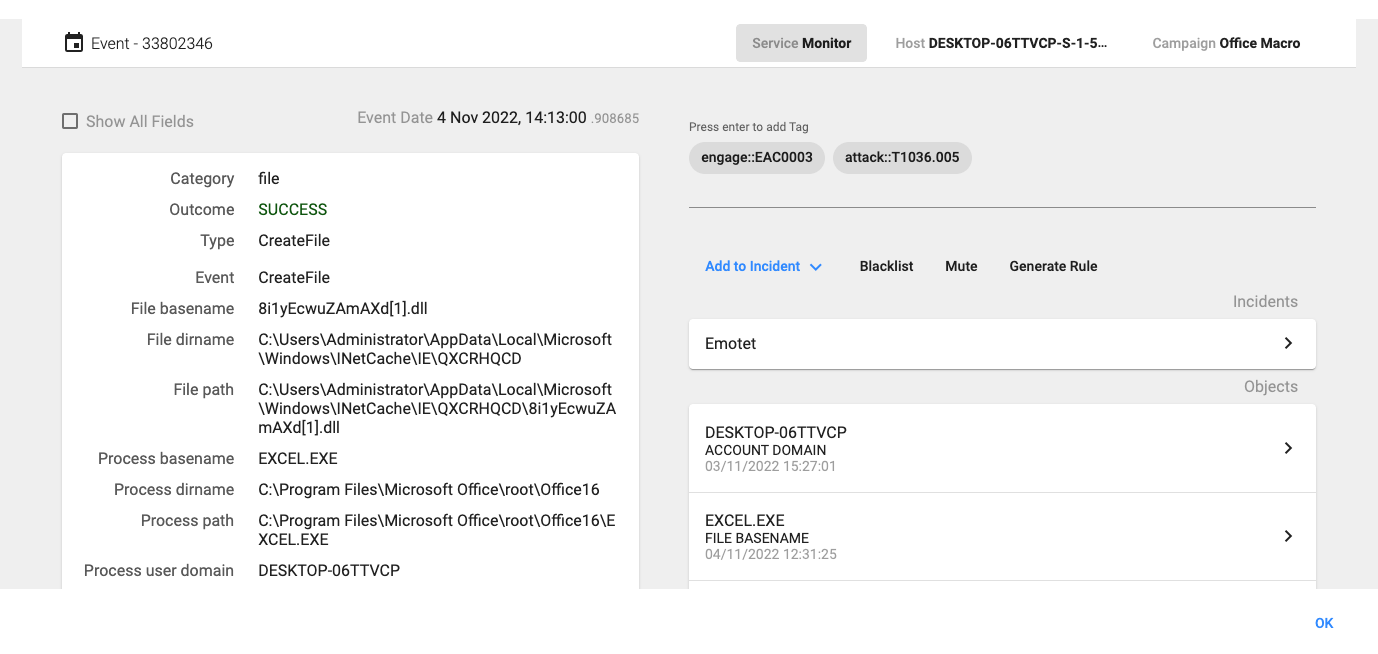
14:13:00:908, the macro downloads the file ‘8i1yEcwuZAmAXd[1].dll’ from the server to the internet temporary cache directory.
14:13:00.915, the macro creates the ‘oxnv1.ooccxx’ file in the user home folder (C:\Users\Administrator\oxnv1.ooccxx).
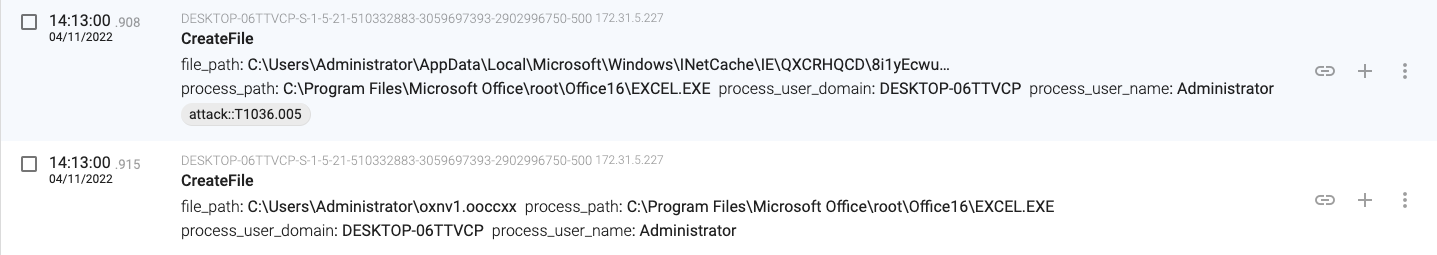
14:13:01.987, the macro launches a new process (regsvr32.exe – PID 2236) that will load the downloaded file (a DLL file).
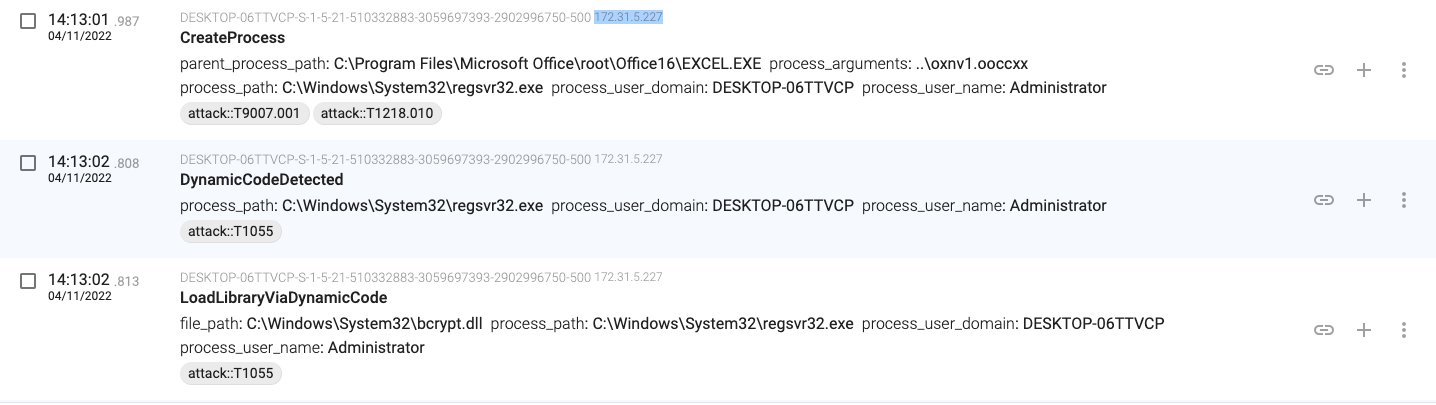
14:13:04.517, the regsvr32.exe(2236) process creates a folder with a random name in C:\Windows\System32

14:13:04.552, the macro connects and downloads content from the ‘greinger-muehle.de’ server (92.204.55.107)
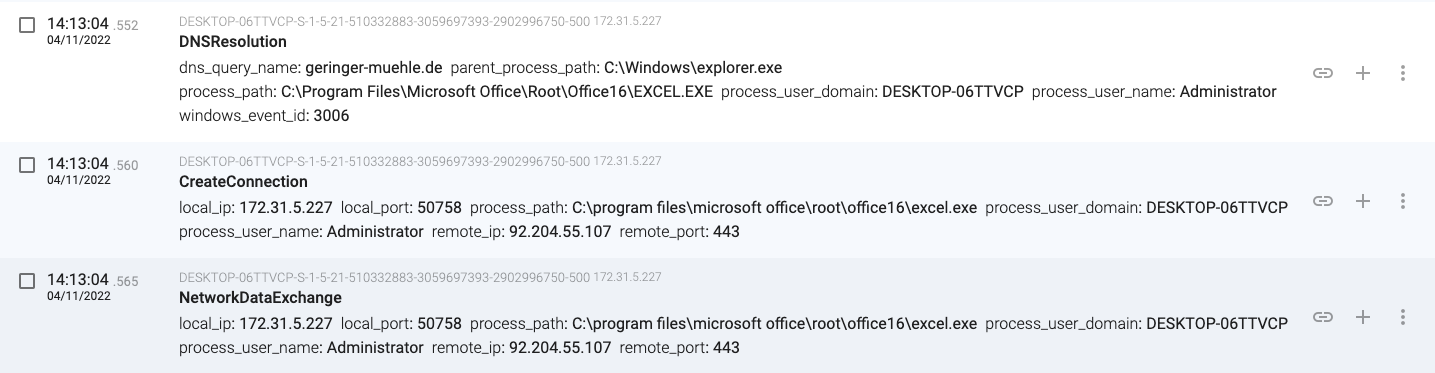
14:13:04.576, the regsvr32.exe(2236) process moves the ‘oxnv1.ooccxx’ file to ‘C:\Windows\System32\AXLbosPUhb\PdWwvRo.dll’

14:13:04.747, the regsvr32.exe(2236) process creates another regsvr32.exe process that loads the DLL.

14:13:05.603, the macro connects and downloads content from ‘intolove.co.uk’ (149.255.58.47)
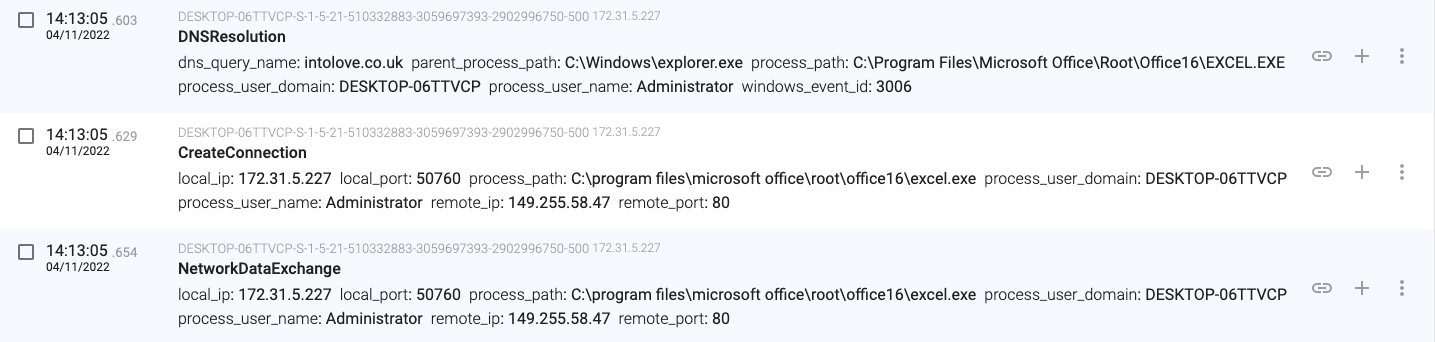
14:13:05.654, the macro stores the downloaded content in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\oxnv3.ooccxx’
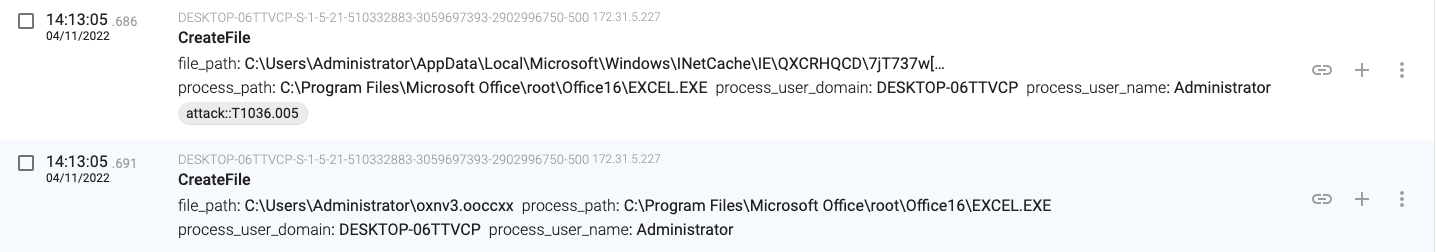
14:13:05.817, the macro launches a new process (regsvr32.exe – PID 1252) that will load the downloaded file (a DLL file).
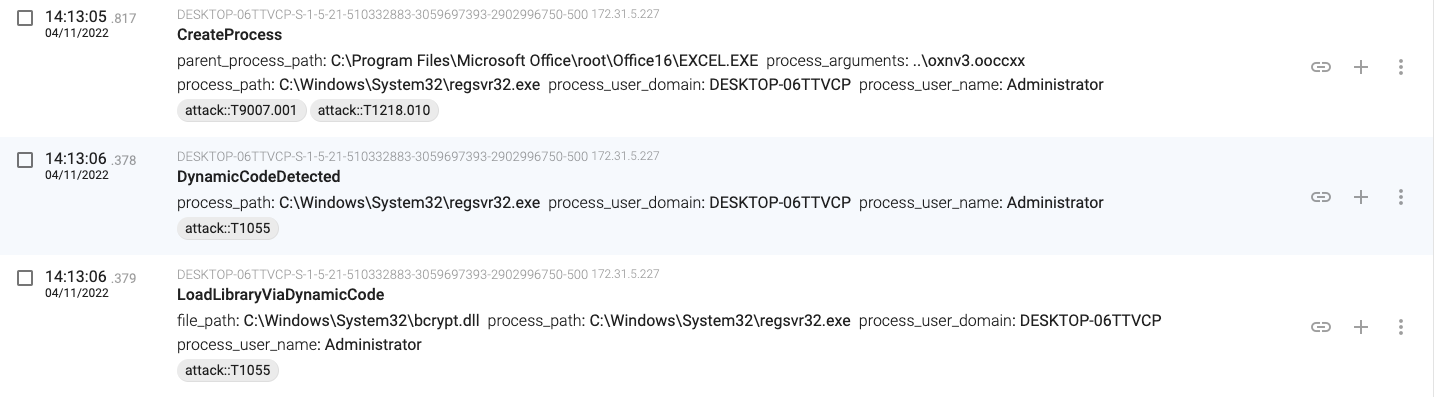
14:13:07.920, the regsvr32.exe(1252) process creates a folder with a random name in C:\Windows\System32

14:13:07.945, the macro connects and downloads content from the ‘isc.net.ua’ server (185.156.41.6)
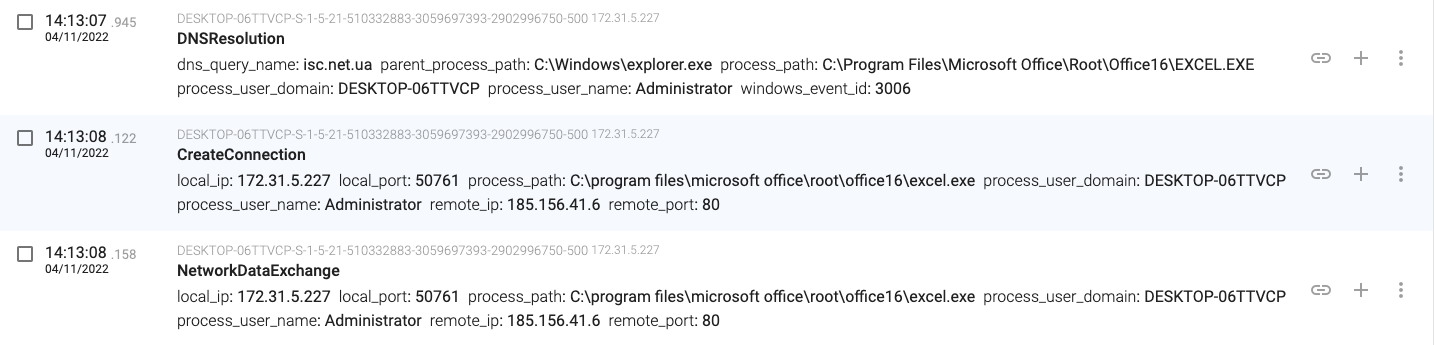
14:13:04.576, the regsvr32.exe(1252) process moves the ‘oxnv3.ooccxx’ file to ‘C:\Windows\System32\JmcciylEQfoOiy\Iuaca.dll

14:13:05.817, the macro launches a new process (regsvr32.exe – PID 840) that will load the downloaded file (a DLL file).

14:13:08.211, the macro stores the downloaded content in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\oxnv4.ooccxx’
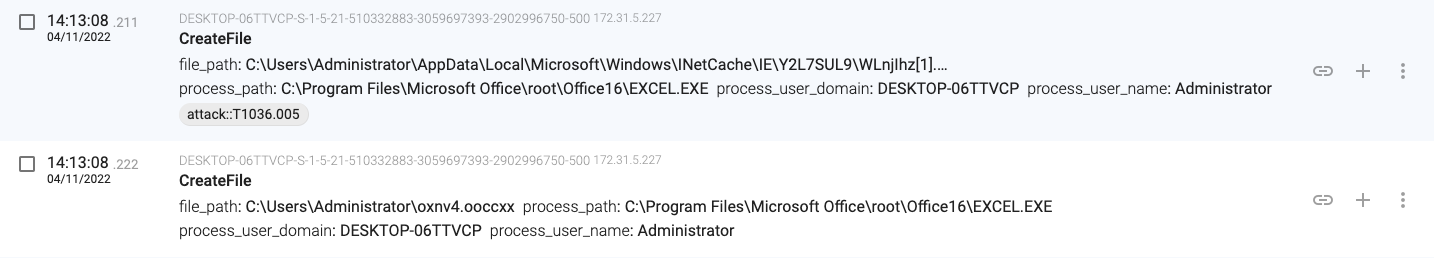
14:13:08.401, the macro launches a new process (regsvr32.exe – PID 1536) that will load the downloaded file (a DLL file).

14:13:12.446, the regsvr32.exe(1536) moves the downloaded file and executes another process loading it
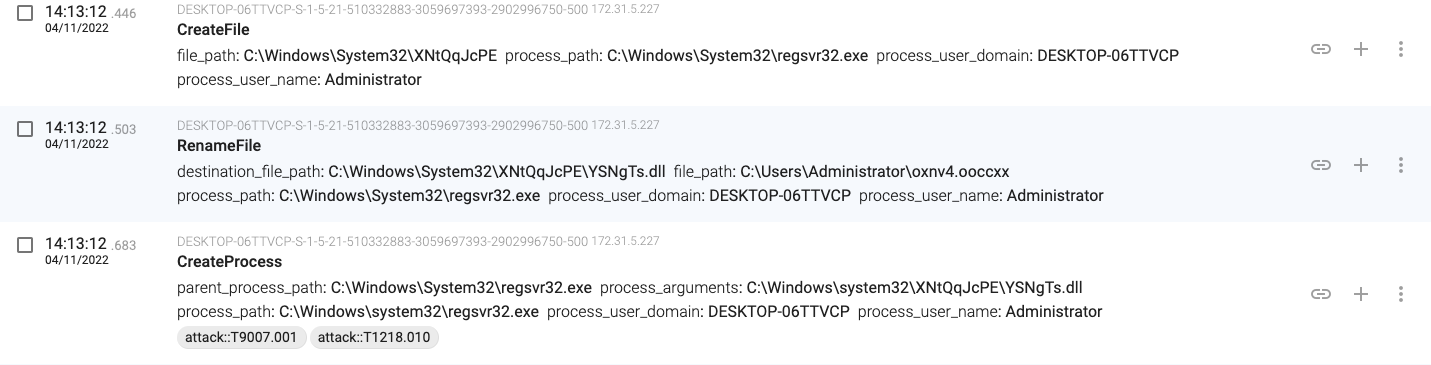
14:13:46, regsvr32.exe(840) downloads a new binary from 182.162.143.56 and stores it in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\elsanrzukqzhla.exe’
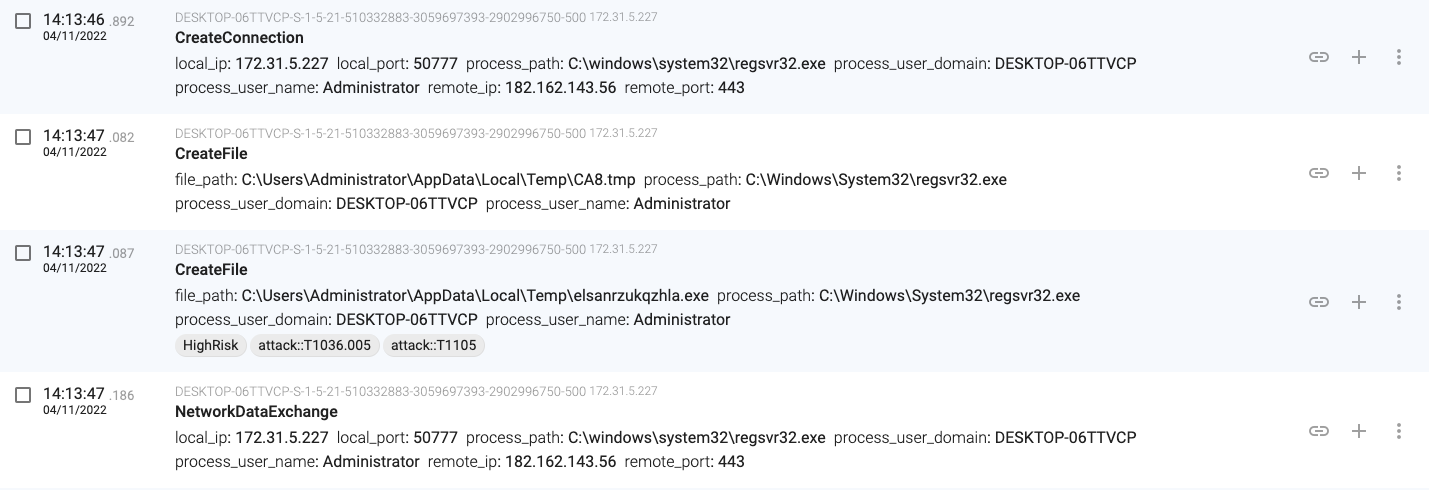
14:13:52.303, regsvr32.exe(840) downloads a new binary from 182.162.143.56 and stores it in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\aaow.exe’
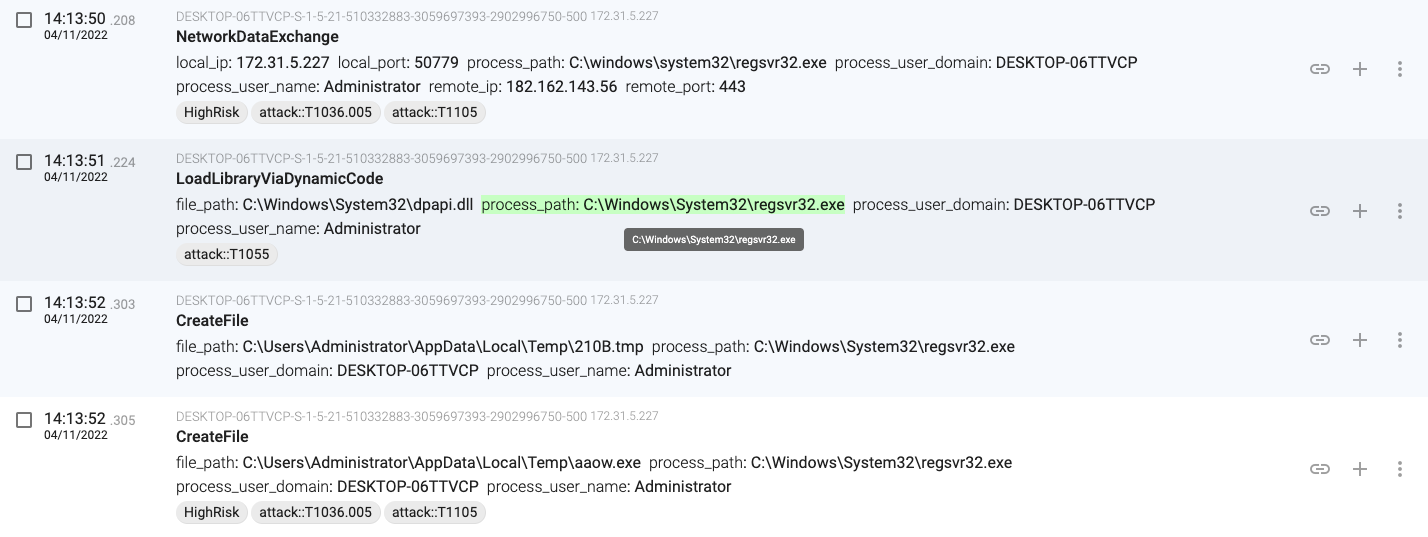
14:13:52.333, regsvr32.exe(9084) establishes persistence by creating a registry key to ‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run’

14:13:52.303, regsvr32.exe(840) downloads a new binary from 182.162.143.56 and stores it in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\bdcktgaba.exe’
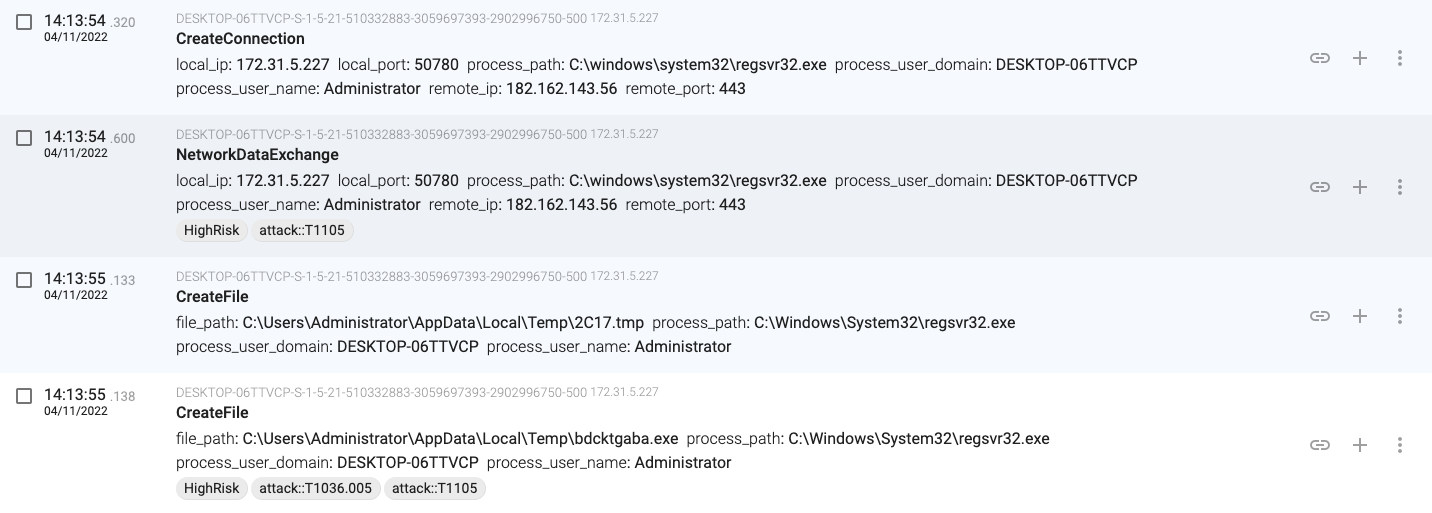
14:14:00.633, regsvr32.exe(1368) establishes persistence by setting the created registry key with name ‘YSNgTs.dll‘ to ‘C:\Windows\system32\XNtQqJcPE\YSNgTs.dll’
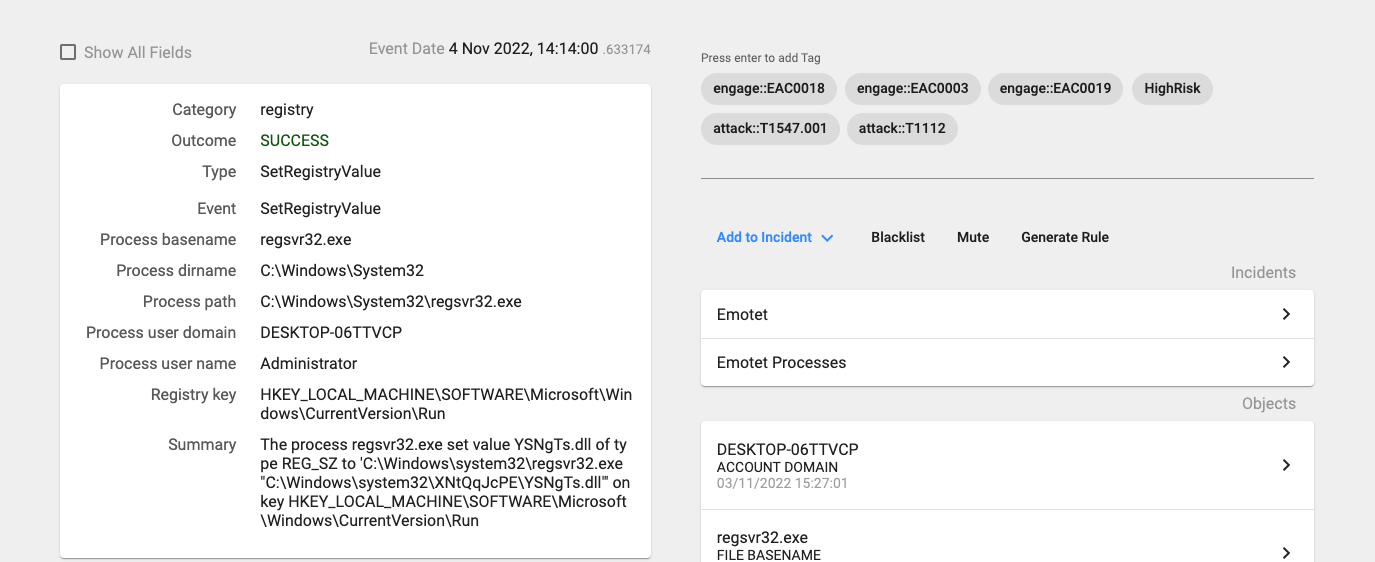
14:14:32.942, regsvr32.exe(1368) downloads a new binary from 182.162.143.56 and stores it in ‘C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Local\Temp\mvgnpvp.exe’
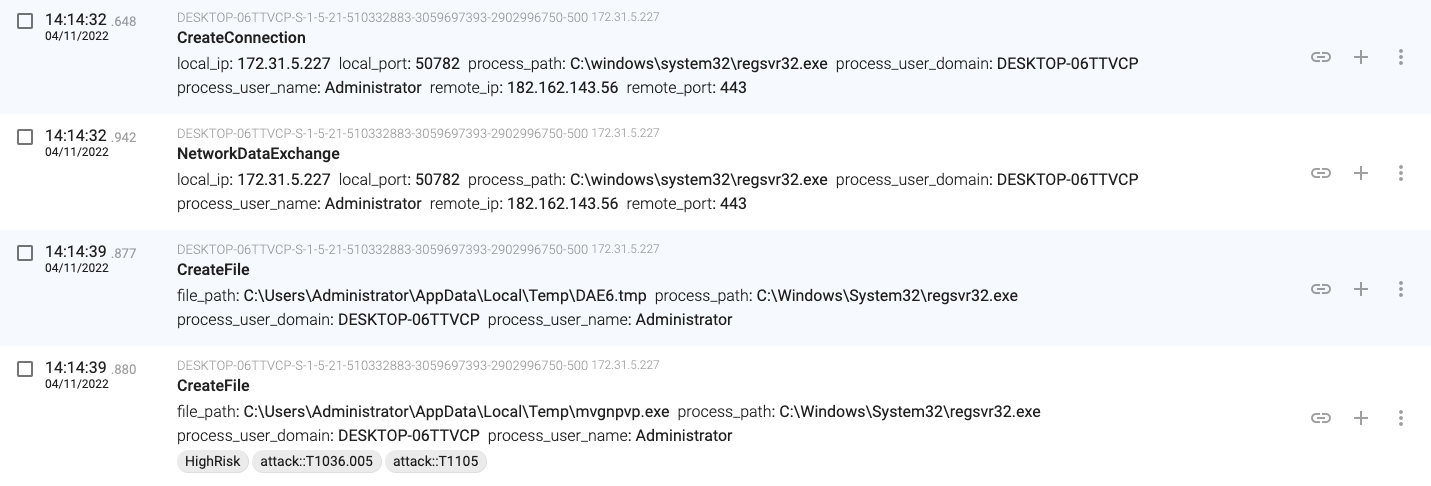
14:16:15.634, regsvr32.exe(1368) creates a new DLL file and launches a process that loads the new file
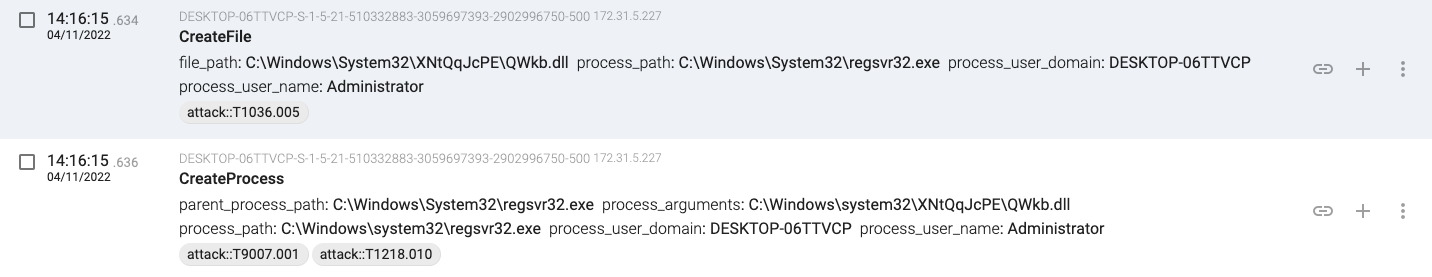
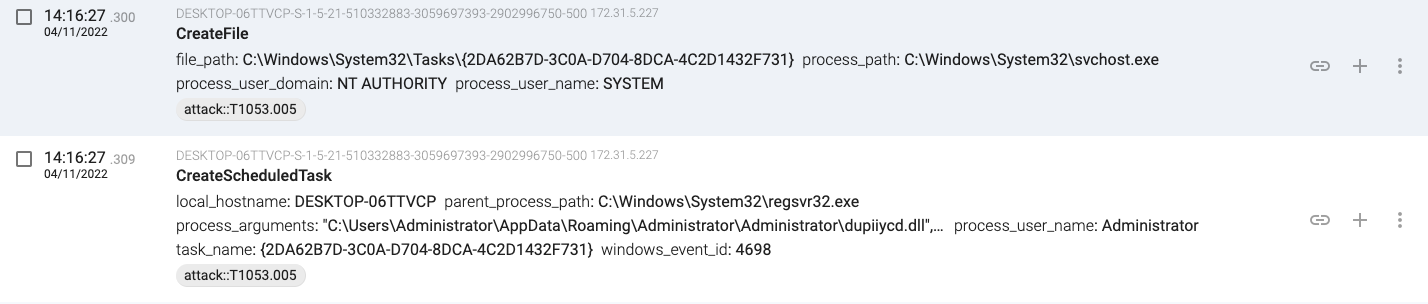
14:16:26.935, regsvr32.exe(7300) creates a new DLL file
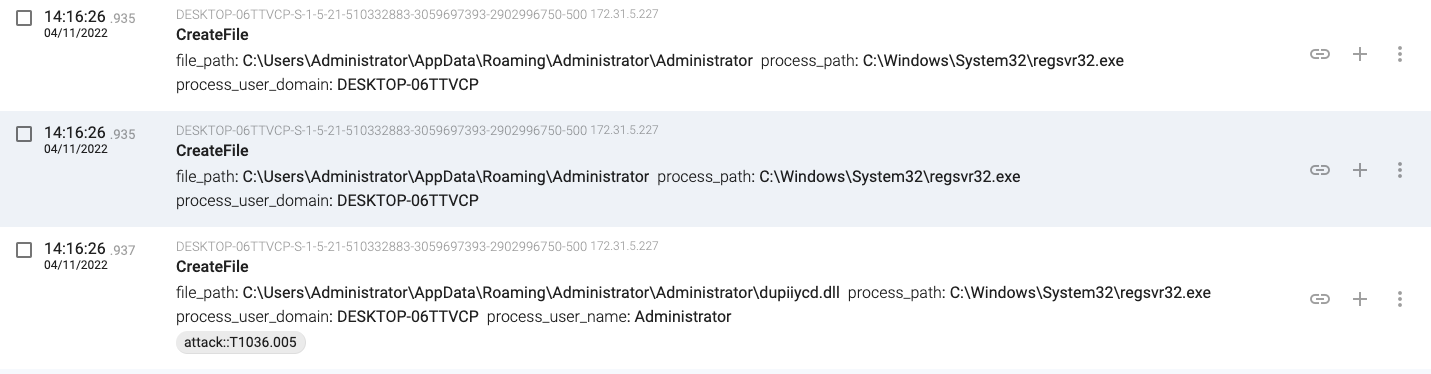
14:16:27.300, regsvr32.exe(7300) adds another persistence mechanism with a scheduled task
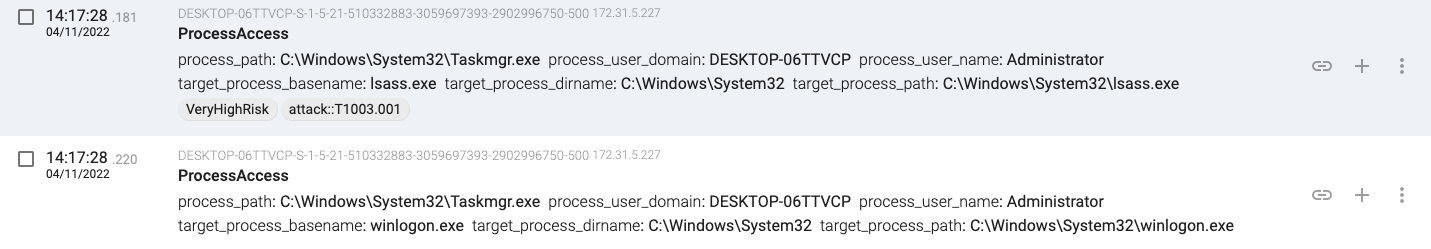
14:17:28.181, taskmgr.exe is used to dump the lsass.exe and winlogon.exe process memory looking for credentials.
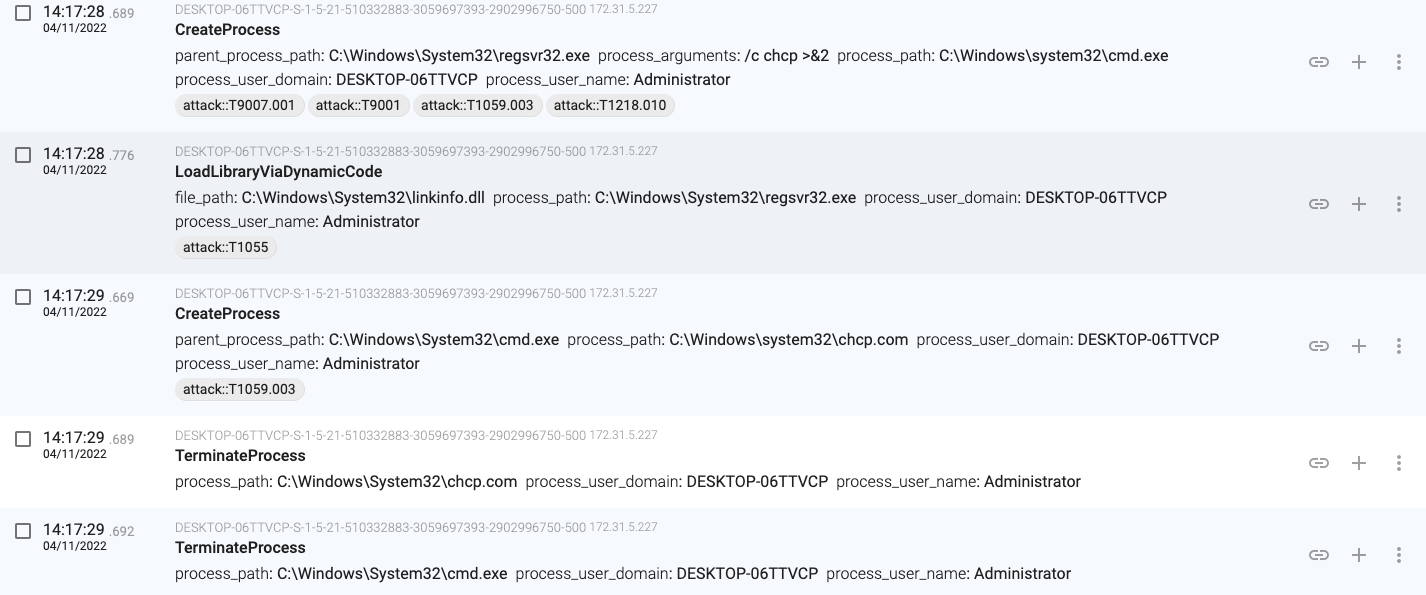
14:17:28.689, regsvr32.exe(68) gets the active code page
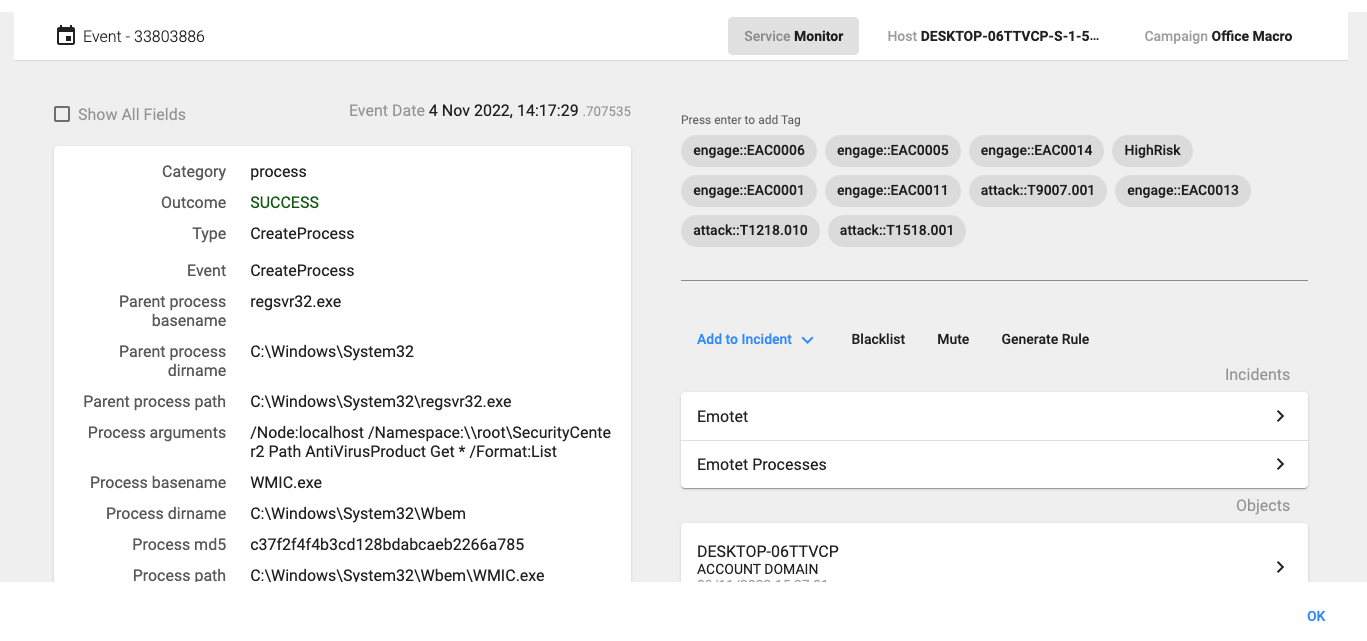
14:17:29.707, regsvr32.exe uses WMI to query for the Antivirus information
14:17:34.230, regsvr32.exe downloads and loads the sqlite64.dll file
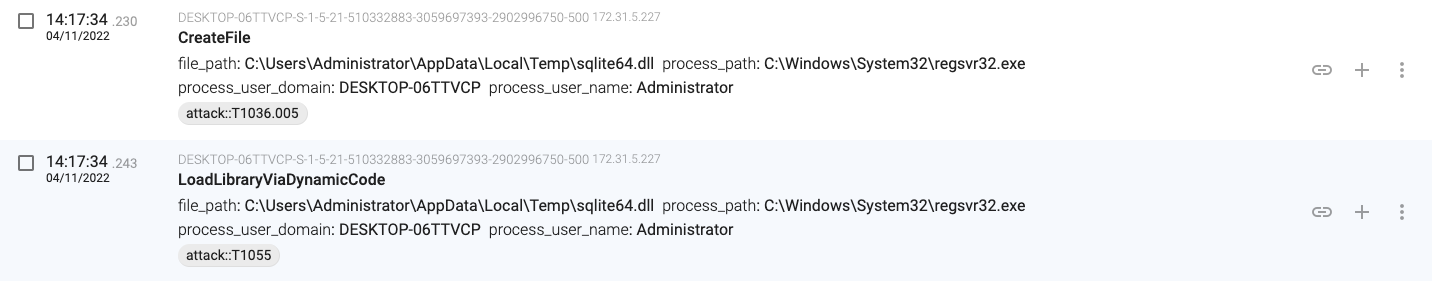
14:17:34.422, regsvr32.exe executes ‘ipconfig.exe /all’

14:17:36.975, regsvr32.exe executes ‘systeminfo.exe’

14:17:39.071, regsvr32.exe executes ‘net config workstation’
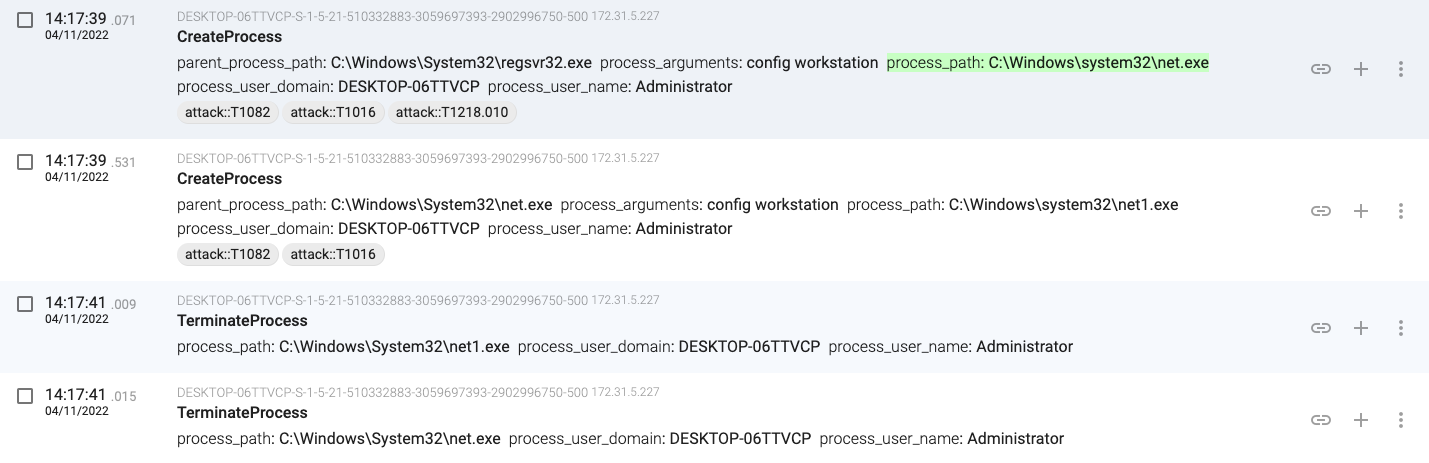
14:17:41.023, regsvr32.exe executes ‘nltest /domain_trusts’ and ‘nltest /domain_trusts /all_trusts’
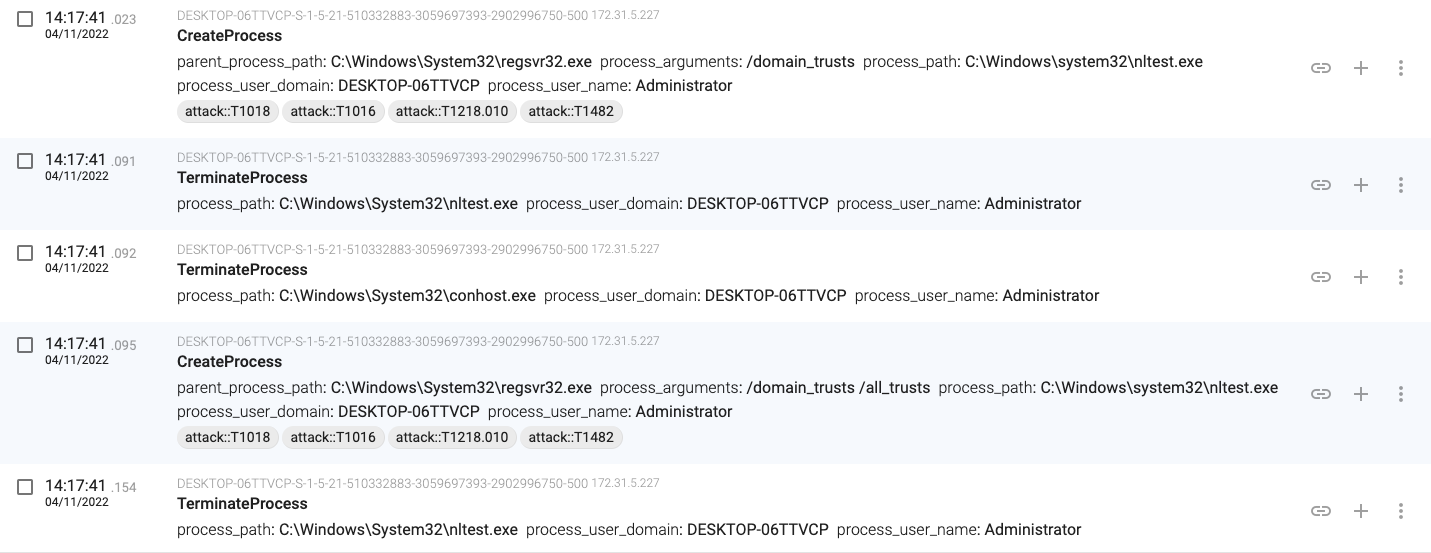
14:17:41.156, regsvr32.exe executes ‘net view /all /domain’

14:18:05.533, regsvr32.exe executes ‘net group “Domain Admins” /domain’
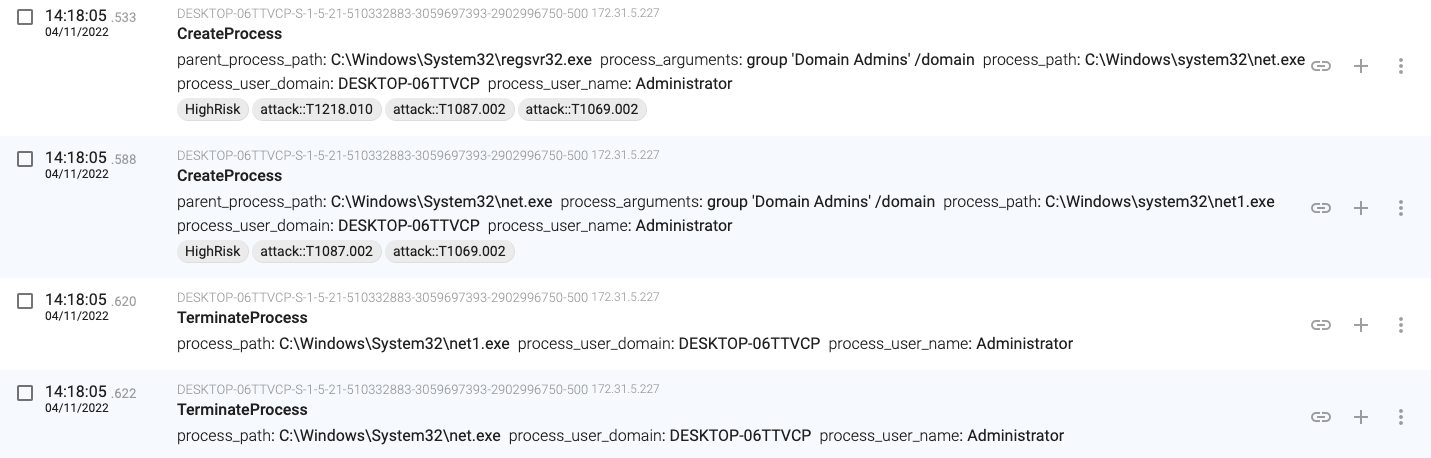
As you can see, the Emotet malware detonates with a gesture as simple as opening a malicious Excel spreadsheet, and the effects can range from data leakage to other malware risks.
If you enjoyed this detailed analysis of an Emotet infection, check out the Threat Intel section of our blog for more deception-powered threat intelligence.


